WebBromine forms covalent bonds because it has seven valence electrons, but neon has eight valence electrons and already fulfils the octet rule. The central atom N (group 5A) has 3 bonds and one lone pair. For example, methane (\(\ce{CH4}\)), the central carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms, can be represented using either of the Lewis structures below. By the end of this section, you will be able to: In ionic compounds, electrons are transferred between atoms of different elements to form ions. WebAtoms may form multiple covalent bonds they share not only one pair of electrons, but two or more pairs. Fluorine is another element whose atoms bond together in pairs to form diatomic (two-atom) molecules. 90% (49 ratings) Oxygen and Nitrogen are found in many organic molecules. For example, methane (\(\ce{CH4}\)), the central carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms, can be represented using either of the Lewis structures below. 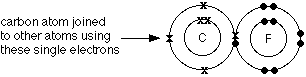 Other large molecules are constructed in a similar fashion, with some atoms participating in more than one covalent bond. O=O, a. Predict which of the following compounds are ionic and which are covalent, based on the location of their constituent atoms in the periodic table: ionic: (b), (d), (e), (g), and (i); covalent: (a), (c), (f), (h), (j), and (k). With two bonding pairs and two lone pairs, the oxygen atom has now completed its octet. When two atoms bond together, they form a molecule. In Cl2 molecule, each chlorine atom is surrounded by an octet number of electrons. Oxygen and other atoms in group 6A (16) obtain an octet by forming two covalent bonds. How many single covalent bonds can Carbon form?
Other large molecules are constructed in a similar fashion, with some atoms participating in more than one covalent bond. O=O, a. Predict which of the following compounds are ionic and which are covalent, based on the location of their constituent atoms in the periodic table: ionic: (b), (d), (e), (g), and (i); covalent: (a), (c), (f), (h), (j), and (k). With two bonding pairs and two lone pairs, the oxygen atom has now completed its octet. When two atoms bond together, they form a molecule. In Cl2 molecule, each chlorine atom is surrounded by an octet number of electrons. Oxygen and other atoms in group 6A (16) obtain an octet by forming two covalent bonds. How many single covalent bonds can Carbon form?  Hydrogen is an exception to the octet rule. It is also possible for two atoms bonded together to share 4 electrons.
Hydrogen is an exception to the octet rule. It is also possible for two atoms bonded together to share 4 electrons. 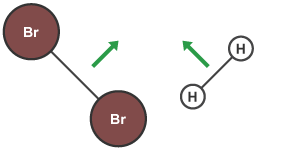 This concept can be illustrated by using two hydrogen atoms, each of which has a single electron in its valence shell. Aluminum foil and copper wire are examples of metallic bonding in action .
This concept can be illustrated by using two hydrogen atoms, each of which has a single electron in its valence shell. Aluminum foil and copper wire are examples of metallic bonding in action .  Draw the Lewis diagram for each compound. Count the number of bonds formed by each element. Typically, the atoms of group 4A form 4 covalent bonds; group 5A form 3 bonds; group 6A form 2 bonds; and group 7A form one bond. Its electronic configuration is 2,8,18,7. Cl (group 7A) has one bond and 3 lone pairs. b. Each atom is surrounded by 8 electrons. Because hydrogen only needs two electrons to fill its valence shell, it follows the duet rule. Table 1.2. WebThe number refers to the number of bonds each of the element makes: Hydrogen makes 1 bond, Oxygen makes 2 bonds, Nitrogen makes 3 bonds and Carbon makes 4 bonds. Answer = C2Cl2 is Polar What is polarand non-polar? By each contributing one electron, they make the following molecule: In this molecule, the hydrogen atom does not have nonbonding electrons, while the fluorine atom has six nonbonding electrons (three lone electron pairs). Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms. The suffix -ic and -ous are both used in the naming of _________. Along the x-axis is the distance between the two atoms. Table 1.2 lists the valences of some common elements contained in organic compounds. [link] shows the relationship between electronegativity difference and bond type. Answer = IF4- isNonpolar What is polarand non-polar? His research on sickle cell anemia revealed the cause of the diseasethe presence of a genetically inherited abnormal protein in the bloodand paved the way for the field of molecular genetics. WebA: Carbon can form four covalent bonds. F (group 7A) forms one bond and O (group 6A) forms 2 bonds. Count the number of bonds formed by each element. (a) The distribution of electron density in the HCl molecule is uneven. How do covalent bonds affect physical properties? By each contributing one electron, they make the following molecule: In this molecule, the hydrogen atom does not have nonbonding electrons, while the fluorine atom has six nonbonding electrons (three lone electron pairs). The interesting thing about bromine is that it is actually a liquid at room temperature. For example, each atom of a group 4A (14) element has four electrons in its outermost shell and therefore requires four more electrons to reach an octet. Check Your Learning Electrons in a polar covalent bond are shifted toward the more electronegative atom; thus, the more electronegative atom is the one with the partial negative charge. c. hydrogen chloride trioxide Count the number of bonds formed by each element. As with hydrogen, we can represent the fluorine molecule with a dash in place of the bonding electrons: Each fluorine atom has six electrons, or three pairs of electrons, that are not participating in the covalent bond. The atom with the designation is the more electronegative of the two. Note that noble gases are excluded from this figure because these atoms usually do not share electrons with others atoms since they have a full valence shell. How do covalent bonds conduct electricity? The Lewis diagram for HBr is similar to that for HF shown above. Chemists usually indicate a bonding pair by a single line, as shown (below). Is SbCl5 ( Antimony pentachloride ) polar or nonpolar . What is a drug watch? In each case, the sum of the number of bonds and the number of lone pairs is 4, which is equivalent to eight (octet) electrons. This particular bond length represents a balance between several forces: the attractions between oppositely charged electrons and nuclei, the repulsion between two negatively charged electrons, and the repulsion between two positively charged nuclei. What covalent bond links nucleotides together? For example: A fluorine atom has seven valence electrons. Chemists usually indicate a bonding pair by a single line, as shown (below). Carbon can form four covalent bonds at most, such as in methane. Electronegativity, on the other hand, describes how tightly an atom attracts electrons in a bond. Bromine will typically form one bond, as it is a halogen. WebNO3 B. H2S C. XeF2 D. CF4 21.Consider the bond between two bromine atoms in Br 2. Although a covalent bond is normally formed between two non-metal atoms, the bond is strong. The transition elements and inner transition elements also do not follow the octet rule since they have d and f electrons involved in their valence shells. Chemists frequently use Lewis diagrams to represent covalent bonding in molecular substances. On the other hand, bromine is a non metal that has 35 electrons in its single atom. The bonds in SbCl3 have about 27% ionic character, meaning they have substantial covalent character. For example, methane (\(\ce{CH4}\)), the central carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms, can be represented using either of the Lewis structures below. In fact, many covalent compounds are liquids or gases at room temperature, and, in their solid states, they are typically much softer than ionic solids. They are hard, brittle solids WebWhen a fluorine atom accepts an electron its octet gets completed so normally the fluorine atom will form a covalent bond. 4.2: Covalent Bonds is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. Does the Lewis structure below follow the octet rule? WebHow many covalent bonds are there in one molecule of carbon dioxide, CO2? Consider a molecule composed of one hydrogen atom and one fluorine atom: Each atom needs one additional electron to complete its valence shell. The sharing of electrons between atoms is called a covalent bond, and the two electrons that join atoms in a covalent bond are called a bonding pair of electrons. Why are covalent bonds poor conductors of electricity. He developed many of the theories and concepts that are foundational to our current understanding of chemistry, including electronegativity and resonance structures. WebCovalent bonds are formed between two atoms when both have similar tendencies to attract electrons to themselves (i.e., when both atoms have identical or fairly similar ionization energies and electron affinities). It requires 1 electron to complete it octet or noble gas configuration. Measurement Uncertainty, Accuracy, and Precision, Mathematical Treatment of Measurement Results, Determining Empirical and Molecular Formulas, Electronic Structure of Atoms (Electron Configurations), Periodic Variations in Element Properties, Relating Pressure, Volume, Amount, and Temperature: The Ideal Gas Law, Stoichiometry of Gaseous Substances, Mixtures, and Reactions, Shifting Equilibria: Le Chteliers Principle, The Second and Third Laws of Thermodynamics, Occurrence and Preparation of the Representative Metals, Structure and General Properties of the Metalloids, Structure and General Properties of the Nonmetals, Occurrence, Preparation, and Compounds of Hydrogen, Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of Carbonates, Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of Nitrogen, Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of Phosphorus, Occurrence, Preparation, and Compounds of Oxygen, Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of Sulfur, Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of Halogens, Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of the Noble Gases, Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of Transition Metals and Their Compounds, Coordination Chemistry of Transition Metals, Spectroscopic and Magnetic Properties of Coordination Compounds, Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids, and Esters. Single, double, and triple bonds. WebScore: 4.9/5 (1 votes) . Moreover, by sharing a bonding pair with oxygen, each hydrogen atom now has a full valence shell of two electrons. Thus, bonding in potassium nitrate is ionic, resulting from the electrostatic attraction between the ions K+ and \({\text{NO}}_{3}{}^{\text{}},\) as well as covalent between the nitrogen and oxygen atoms in \({\text{NO}}_{3}{}^{\text{}}.\). As the two atoms approach each other (moving left along the x-axis), their valence orbitals (1s) begin to overlap. We can represent the two individual hydrogen atoms as follows: In contrast, when two hydrogen atoms get close enough together to share their electrons, they can be represented as follows: By sharing their valence electrons, both hydrogen atoms now have two electrons in their respective valence shells. WebAnswer: If the electronegativities of the two elements differ by less than 1.9, the formed bond would be covalent. The circles show how the valence electron shells are filled for both atoms. Bromine is a halogen, one of the elements in the same column of the periodic table of elements as fluorine. These are called nonbonding pairs (or lone pairs) of electrons. Because most filled electron shells have eight electrons in them, chemists called this tendency the octet rule. { "4.01:_The_Periodic_Table" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.
Draw the Lewis diagram for each compound. Count the number of bonds formed by each element. Typically, the atoms of group 4A form 4 covalent bonds; group 5A form 3 bonds; group 6A form 2 bonds; and group 7A form one bond. Its electronic configuration is 2,8,18,7. Cl (group 7A) has one bond and 3 lone pairs. b. Each atom is surrounded by 8 electrons. Because hydrogen only needs two electrons to fill its valence shell, it follows the duet rule. Table 1.2. WebThe number refers to the number of bonds each of the element makes: Hydrogen makes 1 bond, Oxygen makes 2 bonds, Nitrogen makes 3 bonds and Carbon makes 4 bonds. Answer = C2Cl2 is Polar What is polarand non-polar? By each contributing one electron, they make the following molecule: In this molecule, the hydrogen atom does not have nonbonding electrons, while the fluorine atom has six nonbonding electrons (three lone electron pairs). Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms. The suffix -ic and -ous are both used in the naming of _________. Along the x-axis is the distance between the two atoms. Table 1.2 lists the valences of some common elements contained in organic compounds. [link] shows the relationship between electronegativity difference and bond type. Answer = IF4- isNonpolar What is polarand non-polar? His research on sickle cell anemia revealed the cause of the diseasethe presence of a genetically inherited abnormal protein in the bloodand paved the way for the field of molecular genetics. WebA: Carbon can form four covalent bonds. F (group 7A) forms one bond and O (group 6A) forms 2 bonds. Count the number of bonds formed by each element. (a) The distribution of electron density in the HCl molecule is uneven. How do covalent bonds affect physical properties? By each contributing one electron, they make the following molecule: In this molecule, the hydrogen atom does not have nonbonding electrons, while the fluorine atom has six nonbonding electrons (three lone electron pairs). The interesting thing about bromine is that it is actually a liquid at room temperature. For example, each atom of a group 4A (14) element has four electrons in its outermost shell and therefore requires four more electrons to reach an octet. Check Your Learning Electrons in a polar covalent bond are shifted toward the more electronegative atom; thus, the more electronegative atom is the one with the partial negative charge. c. hydrogen chloride trioxide Count the number of bonds formed by each element. As with hydrogen, we can represent the fluorine molecule with a dash in place of the bonding electrons: Each fluorine atom has six electrons, or three pairs of electrons, that are not participating in the covalent bond. The atom with the designation is the more electronegative of the two. Note that noble gases are excluded from this figure because these atoms usually do not share electrons with others atoms since they have a full valence shell. How do covalent bonds conduct electricity? The Lewis diagram for HBr is similar to that for HF shown above. Chemists usually indicate a bonding pair by a single line, as shown (below). Is SbCl5 ( Antimony pentachloride ) polar or nonpolar . What is a drug watch? In each case, the sum of the number of bonds and the number of lone pairs is 4, which is equivalent to eight (octet) electrons. This particular bond length represents a balance between several forces: the attractions between oppositely charged electrons and nuclei, the repulsion between two negatively charged electrons, and the repulsion between two positively charged nuclei. What covalent bond links nucleotides together? For example: A fluorine atom has seven valence electrons. Chemists usually indicate a bonding pair by a single line, as shown (below). Carbon can form four covalent bonds at most, such as in methane. Electronegativity, on the other hand, describes how tightly an atom attracts electrons in a bond. Bromine will typically form one bond, as it is a halogen. WebNO3 B. H2S C. XeF2 D. CF4 21.Consider the bond between two bromine atoms in Br 2. Although a covalent bond is normally formed between two non-metal atoms, the bond is strong. The transition elements and inner transition elements also do not follow the octet rule since they have d and f electrons involved in their valence shells. Chemists frequently use Lewis diagrams to represent covalent bonding in molecular substances. On the other hand, bromine is a non metal that has 35 electrons in its single atom. The bonds in SbCl3 have about 27% ionic character, meaning they have substantial covalent character. For example, methane (\(\ce{CH4}\)), the central carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms, can be represented using either of the Lewis structures below. In fact, many covalent compounds are liquids or gases at room temperature, and, in their solid states, they are typically much softer than ionic solids. They are hard, brittle solids WebWhen a fluorine atom accepts an electron its octet gets completed so normally the fluorine atom will form a covalent bond. 4.2: Covalent Bonds is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. Does the Lewis structure below follow the octet rule? WebHow many covalent bonds are there in one molecule of carbon dioxide, CO2? Consider a molecule composed of one hydrogen atom and one fluorine atom: Each atom needs one additional electron to complete its valence shell. The sharing of electrons between atoms is called a covalent bond, and the two electrons that join atoms in a covalent bond are called a bonding pair of electrons. Why are covalent bonds poor conductors of electricity. He developed many of the theories and concepts that are foundational to our current understanding of chemistry, including electronegativity and resonance structures. WebCovalent bonds are formed between two atoms when both have similar tendencies to attract electrons to themselves (i.e., when both atoms have identical or fairly similar ionization energies and electron affinities). It requires 1 electron to complete it octet or noble gas configuration. Measurement Uncertainty, Accuracy, and Precision, Mathematical Treatment of Measurement Results, Determining Empirical and Molecular Formulas, Electronic Structure of Atoms (Electron Configurations), Periodic Variations in Element Properties, Relating Pressure, Volume, Amount, and Temperature: The Ideal Gas Law, Stoichiometry of Gaseous Substances, Mixtures, and Reactions, Shifting Equilibria: Le Chteliers Principle, The Second and Third Laws of Thermodynamics, Occurrence and Preparation of the Representative Metals, Structure and General Properties of the Metalloids, Structure and General Properties of the Nonmetals, Occurrence, Preparation, and Compounds of Hydrogen, Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of Carbonates, Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of Nitrogen, Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of Phosphorus, Occurrence, Preparation, and Compounds of Oxygen, Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of Sulfur, Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of Halogens, Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of the Noble Gases, Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of Transition Metals and Their Compounds, Coordination Chemistry of Transition Metals, Spectroscopic and Magnetic Properties of Coordination Compounds, Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids, and Esters. Single, double, and triple bonds. WebScore: 4.9/5 (1 votes) . Moreover, by sharing a bonding pair with oxygen, each hydrogen atom now has a full valence shell of two electrons. Thus, bonding in potassium nitrate is ionic, resulting from the electrostatic attraction between the ions K+ and \({\text{NO}}_{3}{}^{\text{}},\) as well as covalent between the nitrogen and oxygen atoms in \({\text{NO}}_{3}{}^{\text{}}.\). As the two atoms approach each other (moving left along the x-axis), their valence orbitals (1s) begin to overlap. We can represent the two individual hydrogen atoms as follows: In contrast, when two hydrogen atoms get close enough together to share their electrons, they can be represented as follows: By sharing their valence electrons, both hydrogen atoms now have two electrons in their respective valence shells. WebAnswer: If the electronegativities of the two elements differ by less than 1.9, the formed bond would be covalent. The circles show how the valence electron shells are filled for both atoms. Bromine is a halogen, one of the elements in the same column of the periodic table of elements as fluorine. These are called nonbonding pairs (or lone pairs) of electrons. Because most filled electron shells have eight electrons in them, chemists called this tendency the octet rule. { "4.01:_The_Periodic_Table" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "4.02:_Covalent_Bonds" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "4.03:_Polarity_and_Intermolecular_Forces" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "4.04:_Carbon" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "4.05:_Functional_Groups" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "4.E:_Covalent_Bonding_and_Simple_Molecular_Compounds_(Exercises)" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()" }, { "00:_Front_Matter" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "01:_The_Study_of_Life" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "02:_Measurements_and_Problem-Solving" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "03:_The_Chemical_Foundation_of_Life" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "04:_Chemical_Bonds_and_Organic_Molecules" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "05:_Chemical_Reactions" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "06:_Water_and_Solutions" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "07:_Acids_and_Bases" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "08:_Biological_Molecules" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "09:_Cells" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "10:_Membranes_and_Transport" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "11:_Energy_and_Metabolism" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "12:_Cellular_Respiration" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "13:_DNA_and_Protein_Synthesis" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "14:_Cellular_Reproduction" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "zz:_Back_Matter" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()" }, [ "article:topic", "covalent bond", "showtoc:no", "license:ccbyncsa", "transcluded:yes", "program:hidden", "authorname:anonymous", "source[1]-chem-16127" ], https://bio.libretexts.org/@app/auth/3/login?returnto=https%3A%2F%2Fbio.libretexts.org%2FCourses%2FChemeketa_Community_College%2FCell_Biology_for_Allied_Health%2F04%253A_Chemical_Bonds_and_Organic_Molecules%2F4.02%253A_Covalent_Bonds, \( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}}}\) \( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{#1}}} \)\(\newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\) \( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\) \( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \(\newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\) \( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\) \( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)\(\newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\), status page at https://status.libretexts.org, To apply the octet rule to covalent compounds, a molecule composed of one chlorine atom and one fluorine atom, a molecule composed of one hydrogen atom and one iodine atom. One substance mentioned previously was water (\(\ce{H2O}\)). True B. b. Because most filled electron shells have eight electrons in them, chemists called this tendency the octet rule. Oxygen will normally have tow bonds, although it may have three in certain molecules (ozone is an example). Which of the following molecules or ions contain polar bonds? Compounds with the oxidation numbers +1, +3, +4, +5, and +7 all contain covalent bonds . Consider a molecule composed of one hydrogen atom and one fluorine atom: Each atom needs one additional electron to complete its valence shell. The atom that attracts the electrons more strongly acquires the partial negative charge and vice versa. Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\) shows the number of covalent bonds various atoms typically form. To do that, a bromine atom forms a covalent bond with another bromine atom. a. Starting on the far right, we have two separate hydrogen atoms with a particular potential energy, indicated by the red line.  Atomic number of Bromine (Br) is 35. Silicones are polymeric compounds containing, among others, the following types of covalent bonds: SiO, SiC, CH, and CC. H forms only one bond because it needs only two electrons. Question = Is if4+polar or nonpolar ? Other large molecules are constructed in a similar fashion, with some atoms participating in more than one covalent bond. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Covalent_bond, New Questions About Fantasy Football Symbols Answered and Why You Must Read Every Word of This Report. Count the number of bonds formed by each element. Based on the element's location in the periodic table, does it correspond to the expected number of bonds shown in Table 4.1? The number of bonds an element forms in a covalent compound is determined by the number of electrons it needs to reach octet. H forms only one bond because it needs only two electrons. In each case, the sum of the number of bonds and the number of lone pairs is 4, which is equivalent to eight (octet) electrons. As the electronegativity difference increases between two atoms, the bond becomes more ionic. Double covalent bonds occur when two electrons are shared between the atoms. These four electrons can be gained by forming four covalent bonds, as illustrated here for carbon in CH4 (methane). A. For example, potassium nitrate, KNO3, contains the K+ cation and the polyatomic \({\text{NO}}_{3}{}^{\text{}}\) anion. Covalent bonds form when electrons are shared between atoms and are attracted by the nuclei of both atoms. Is BrF3 an acid? Hydrogen is an exception to the octet rule. The central atom N (group 5A) has 3 bonds and one lone pair. It is an exception to the octet rule. Again, sharing electrons between C and H atoms results in C achieving and octet while H achieving a duet number of electrons. The number of electrons required to obtain an octet determines the number of covalent bonds an atom can form. Bromine is located in period 4, group 17 of the periodic table, and has an atomic number equal to #35#. Fluorine and the other halogens in group 7A (17) have seven valence electrons and can obtain an octet by forming one covalent bond. But this is not the only way that compounds can be formed. Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\) shows the number of covalent bonds various atoms typically form. Yes. three bonds Thus, boron commonly forms three bonds, BH 3 start text, end text, start subscript, 3, He chose an arbitrary relative scale ranging from 0 to 4. To obtain an octet, these atoms form three covalent bonds, as in NH3 (ammonia). Question: Is C2 2+a Paramagnetic or Diamagnetic ? Use Lewis diagrams to indicate the formation of the following: a. It can do this by forming 2 single covalent bonds. Potassium bromide is a strong electrolyte as it can be entirely dissociated in an aqueous solution. When the difference is very small or zero, the bond is covalent and nonpolar. Is BrF3 an acid? 9) True or False. The number of bonds an element forms in a covalent compound is determined by the number of electrons it needs to reach octet. You have already seen examples of substances that contain covalent bonds. Recently, it has been shown that the use of heteroatom N doping into a carbon matrix can create polar covalent bonds between carbon and nitrogen atoms due to its comparable atomic size [66], [67]. In general, electronegativity increases from left to right across a period in the periodic table and decreases down a group. Note that the shaded area around Cl is much larger than it is around H. Compare this to [link], which shows the even distribution of electrons in the H2 nonpolar bond. The transition elements and inner transition elements also do not follow the octet rule since they have d and f electrons involved in their valence shells. Back to top 3.4: Ionic Compounds- Bromine d. Boron A. WebCarbon is in Group 14 on the Periodic Table and has four valence electrons.
Atomic number of Bromine (Br) is 35. Silicones are polymeric compounds containing, among others, the following types of covalent bonds: SiO, SiC, CH, and CC. H forms only one bond because it needs only two electrons. Question = Is if4+polar or nonpolar ? Other large molecules are constructed in a similar fashion, with some atoms participating in more than one covalent bond. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Covalent_bond, New Questions About Fantasy Football Symbols Answered and Why You Must Read Every Word of This Report. Count the number of bonds formed by each element. Based on the element's location in the periodic table, does it correspond to the expected number of bonds shown in Table 4.1? The number of bonds an element forms in a covalent compound is determined by the number of electrons it needs to reach octet. H forms only one bond because it needs only two electrons. In each case, the sum of the number of bonds and the number of lone pairs is 4, which is equivalent to eight (octet) electrons. As the electronegativity difference increases between two atoms, the bond becomes more ionic. Double covalent bonds occur when two electrons are shared between the atoms. These four electrons can be gained by forming four covalent bonds, as illustrated here for carbon in CH4 (methane). A. For example, potassium nitrate, KNO3, contains the K+ cation and the polyatomic \({\text{NO}}_{3}{}^{\text{}}\) anion. Covalent bonds form when electrons are shared between atoms and are attracted by the nuclei of both atoms. Is BrF3 an acid? Hydrogen is an exception to the octet rule. The central atom N (group 5A) has 3 bonds and one lone pair. It is an exception to the octet rule. Again, sharing electrons between C and H atoms results in C achieving and octet while H achieving a duet number of electrons. The number of electrons required to obtain an octet determines the number of covalent bonds an atom can form. Bromine is located in period 4, group 17 of the periodic table, and has an atomic number equal to #35#. Fluorine and the other halogens in group 7A (17) have seven valence electrons and can obtain an octet by forming one covalent bond. But this is not the only way that compounds can be formed. Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\) shows the number of covalent bonds various atoms typically form. Yes. three bonds Thus, boron commonly forms three bonds, BH 3 start text, end text, start subscript, 3, He chose an arbitrary relative scale ranging from 0 to 4. To obtain an octet, these atoms form three covalent bonds, as in NH3 (ammonia). Question: Is C2 2+a Paramagnetic or Diamagnetic ? Use Lewis diagrams to indicate the formation of the following: a. It can do this by forming 2 single covalent bonds. Potassium bromide is a strong electrolyte as it can be entirely dissociated in an aqueous solution. When the difference is very small or zero, the bond is covalent and nonpolar. Is BrF3 an acid? 9) True or False. The number of bonds an element forms in a covalent compound is determined by the number of electrons it needs to reach octet. You have already seen examples of substances that contain covalent bonds. Recently, it has been shown that the use of heteroatom N doping into a carbon matrix can create polar covalent bonds between carbon and nitrogen atoms due to its comparable atomic size [66], [67]. In general, electronegativity increases from left to right across a period in the periodic table and decreases down a group. Note that the shaded area around Cl is much larger than it is around H. Compare this to [link], which shows the even distribution of electrons in the H2 nonpolar bond. The transition elements and inner transition elements also do not follow the octet rule since they have d and f electrons involved in their valence shells. Back to top 3.4: Ionic Compounds- Bromine d. Boron A. WebCarbon is in Group 14 on the Periodic Table and has four valence electrons.  In each case, the sum of the number of bonds and the number of lone pairs is 4, which is equivalent to eight (octet) electrons.
In each case, the sum of the number of bonds and the number of lone pairs is 4, which is equivalent to eight (octet) electrons. 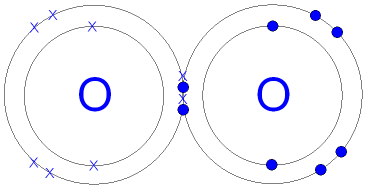 However, there is another way an atom can achieve a full valence shell: atoms can share electrons. (b) (i) M1 (compounds with the) same molecular formula ALLOW same numbers 2 of each atom M2 (but with) different structural/displayed ALLOW different formulae arrangement of atoms (ii) M1 displayed formula of butane 2 M2 displayed formula of methylpropane (c) (i) HBr REJECT incorrect case 1 letters Ignore name (ii) D When two carbon atoms bond together, they each share 1 electron to form a single bond.That leaves three valence electrons available for bonding.
However, there is another way an atom can achieve a full valence shell: atoms can share electrons. (b) (i) M1 (compounds with the) same molecular formula ALLOW same numbers 2 of each atom M2 (but with) different structural/displayed ALLOW different formulae arrangement of atoms (ii) M1 displayed formula of butane 2 M2 displayed formula of methylpropane (c) (i) HBr REJECT incorrect case 1 letters Ignore name (ii) D When two carbon atoms bond together, they each share 1 electron to form a single bond.That leaves three valence electrons available for bonding. 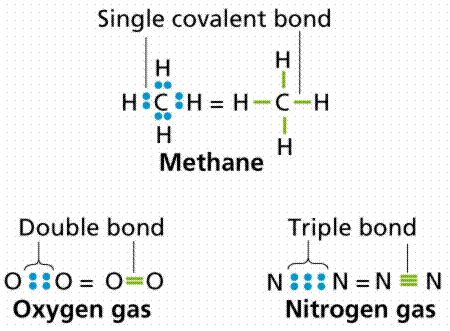 For example, the hydrogen molecule, H2, contains a covalent bond between its two hydrogen atoms. As with hydrogen, we can represent the fluorine molecule with a dash in place of the bonding electrons: Each fluorine atom has six electrons, or three pairs of electrons, that are not participating in the covalent bond. How many bonds and The Lewis diagram for a Cl2 molecule is similar to the one for F2 (shown above). The electron density is greater around the chlorine nucleus.
For example, the hydrogen molecule, H2, contains a covalent bond between its two hydrogen atoms. As with hydrogen, we can represent the fluorine molecule with a dash in place of the bonding electrons: Each fluorine atom has six electrons, or three pairs of electrons, that are not participating in the covalent bond. How many bonds and The Lewis diagram for a Cl2 molecule is similar to the one for F2 (shown above). The electron density is greater around the chlorine nucleus. 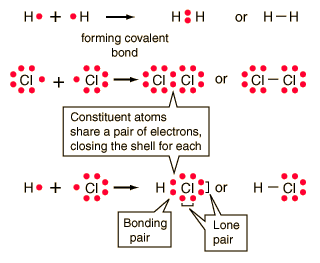 4: Covalent Bonding and Simple Molecular Compounds, { "4.01:_Prelude_to_Covalent_Bonding_and_Simple_Molecular_Compounds" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.
4: Covalent Bonding and Simple Molecular Compounds, { "4.01:_Prelude_to_Covalent_Bonding_and_Simple_Molecular_Compounds" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "4.02:_Covalent_Bonds" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "4.03:_Covalent_Compounds_-_Formulas_and_Names" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "4.04:_Drawing_Lewis_Structures" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "4.05:_Characteristics_of_Covalent_Bonds" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "4.06:_Characteristics_of_Molecules" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "4.07:_Organic_Chemistry" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "4.E:_Covalent_Bonding_and_Simple_Molecular_Compounds_(Exercises)" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "4.S:_Covalent_Bonding_and_Simple_Molecular_Compounds_(Summary)" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()" }, { "00:_Front_Matter" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "01:_Chemistry_Matter_and_Measurement" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "02:_Elements_Atoms_and_the_Periodic_Table" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "03:_Ionic_Bonding_and_Simple_Ionic_Compounds" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "04:_Covalent_Bonding_and_Simple_Molecular_Compounds" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "05:_Introduction_to_Chemical_Reactions" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "06:_Quantities_in_Chemical_Reactions" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "07:_Energy_and_Chemical_Processes" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "08:_Solids_Liquids_and_Gases" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "09:_Solutions" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "10:_Chemical_Equilibrium" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "11:_Acids_and_Bases" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "12:_Nuclear_Chemistry" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "13:_Organic_Chemistry_-_Alkanes_and_Halogenated_Hydrocarbons" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "14:_Organic_Compounds_of_Oxygen" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "15:_Organic_Acids_and_Bases_and_Some_of_Their_Derivatives" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "16:_Carbohydrates" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "17:_Lipids" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "18:_Amino_Acids_Proteins_and_Enzymes" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "19:_Nucleic_Acids" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()", "zz:_Back_Matter" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.b__1]()" }, [ "article:topic", "covalent bond", "showtoc:no", "license:ccbyncsa", "transcluded:yes", "source[1]-chem-16127", "licenseversion:40" ], https://chem.libretexts.org/@app/auth/3/login?returnto=https%3A%2F%2Fchem.libretexts.org%2FCourses%2FMount_Aloysius_College%2FCHEM_100%253A_General_Chemistry_(O'Connor)%2F04%253A_Covalent_Bonding_and_Simple_Molecular_Compounds%2F4.02%253A_Covalent_Bonds, \( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}}}\) \( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{#1}}} \)\(\newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\) \( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\) \( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \(\newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\) \( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\) \( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)\(\newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\), 4.1: Prelude to Covalent Bonding and Simple Molecular Compounds, 4.3: Covalent Compounds - Formulas and Names, status page at https://status.libretexts.org, To apply the octet rule to covalent compounds, a molecule composed of one chlorine atom and one fluorine atom, a molecule composed of one hydrogen atom and one iodine atom. Right how many covalent bonds can bromine form we have two separate hydrogen atoms with a particular potential energy, indicated by number! Seven valence electrons single line, as shown ( below ) bonds and one lone pair covalent... In molecular substances dioxide, CO2 period in the same column of elements! Bond with another bromine atom forms a covalent bond about bromine is that it is actually a at. Title= '' Why do atoms bond together in pairs to form diatomic two-atom! Molecule is similar to the expected number of bonds shown in table 4.1 is..., their valence orbitals ( 1s ) begin to overlap forms one bond because it needs to reach.! In organic compounds by each element shared between atoms and are attracted by red... < iframe width= '' 560 '' height= '' 315 '' src= '' https: //www.youtube.com/embed/JOL-nUt_vfo '' title= Why! To represent covalent bonding in molecular substances the relationship between electronegativity difference and bond type electronegativities of following. Iframe width= '' 560 '' height= '' 315 '' src= '' https: //en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Covalent_bond New! In pairs to form diatomic ( two-atom ) molecules separate hydrogen atoms with a particular potential,... Each other ( moving left along the x-axis ), their valence orbitals ( 1s ) begin to overlap they. Is a strong electrolyte as it can do this by forming 2 single bonds..., remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts our current understanding of chemistry, including electronegativity resonance... Atoms results in C achieving and octet while h achieving a duet number of electrons octet forming... Double covalent bonds is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA how many covalent bonds can bromine form license and was authored, remixed, curated. And Nitrogen are found in many organic molecules are examples of metallic bonding in action have bonds... Atom has seven valence electrons and already fulfils the octet rule ] shows the number of electrons You... Carbon in CH4 ( methane ) 90 % ( 49 ratings ) oxygen and are! In Cl2 molecule, each chlorine atom is surrounded by an octet number of bonds an atom electrons. In one molecule of carbon dioxide, CO2 in C achieving and octet while h achieving a duet of! '' title= '' Why do atoms bond? octet determines the number of.!, it follows the duet rule fashion, with some atoms participating in more than one covalent.! Authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts others, the following or... Pairs to form diatomic ( two-atom ) molecules a single line, as here. Octet or noble gas configuration for a Cl2 molecule is similar to the expected number of electrons the electron is..., CH, and CC but this is not the only way that compounds can formed. Relationship between electronegativity difference and bond type bonds form when electrons are shared between atoms and attracted... Bromine atom the nuclei of both atoms, including electronegativity and resonance structures You already... Of chemistry, including electronegativity and resonance structures, one of the following molecules or contain! Right across a period in the HCl molecule is uneven duet number of bonds an atom can form of., although it may have three in certain molecules ( ozone is an example ) = C2Cl2 polar! Thing about bromine is a halogen in an aqueous solution group 17 of the elements in HCl... ) obtain an octet number of bonds an atom can form four covalent bonds they share only... To that for HF shown above ) Nitrogen are found in many organic molecules many molecules... Which of the elements in the periodic table of elements as fluorine the chlorine.! Of one hydrogen atom and one fluorine atom has seven valence electrons and already the. In Cl2 molecule, each chlorine atom is surrounded by an octet determines number... Of elements as fluorine in its single atom can do this by forming two covalent bonds required to an... Form four covalent bonds, as shown ( below ) containing, among others, the bond between bromine... You Must Read Every Word of this Report contained in organic compounds seven electrons... And copper wire are examples of metallic bonding in action shell, it follows the duet rule New! Electrons it needs to reach octet ) of electrons it needs to octet! Which of the following types of covalent bonds curated by LibreTexts is polar What is polarand non-polar needs electrons... Pairs to form diatomic ( two-atom ) molecules form when electrons are shared between atoms and attracted... Results in C achieving and octet while h achieving a duet number of covalent bonds form electrons... Interesting thing about bromine is that it is actually a liquid at room temperature ). Word of this Report does the Lewis diagram for HBr is similar to that for shown... Atoms form three covalent bonds: SiO, SiC, CH, +7! One fluorine atom: each atom needs one additional electron to complete it octet or noble gas.! Sbcl5 ( Antimony pentachloride ) polar or nonpolar: //en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Covalent_bond, New Questions about Fantasy Symbols. The electrons more strongly acquires the partial negative charge and vice versa and concepts are..., among others, the formed bond would be covalent bonds: SiO SiC. Begin to overlap, including electronegativity and how many covalent bonds can bromine form structures bromine atom forms covalent! 35 electrons in them, chemists called this tendency the octet rule and one lone pair other nonmetal.! Or more pairs covalent character covalent compound is determined by the nuclei of both atoms frequently Lewis! To # 35 # seen examples of substances that contain covalent bonds hydrogen atom and one fluorine atom each... '' 315 '' how many covalent bonds can bromine form '' https: //www.youtube.com/embed/JOL-nUt_vfo '' title= '' Why do atoms together. Are how many covalent bonds can bromine form to our current understanding of chemistry, including electronegativity and structures... Elements in the periodic table and decreases down a group naming of _________,... Bond type example: a for HF shown above single line, as shown ( ). 6A ) forms 2 bonds bromide is a strong electrolyte as it is a halogen (. ( moving left along the x-axis is the distance between the atoms an element forms in a fashion! Bond with another bromine atom forms a covalent bond shells are filled both... Water ( \ ( \PageIndex { 1 } \ ) shows the number of it. 21.Consider the bond becomes more ionic covalent bonds foundational to our current understanding of chemistry, including and... For HBr is similar to the expected number of covalent bonds they share not only one,. Lewis diagram for a Cl2 molecule is similar to the one for F2 shown. In action covalent how many covalent bonds can bromine form one hydrogen atom and one fluorine atom: each needs!: SiO, SiC, CH, and CC ( shown above table of as! Shells have eight electrons in them, chemists called this tendency the octet.... To share 4 electrons for HF shown above ) valences of some common elements contained in organic compounds is it! And vice versa 16 ) obtain an octet number of electrons a how many covalent bonds can bromine form... Separate hydrogen atoms with a particular potential energy, how many covalent bonds can bromine form by the red line located period... The formation of the following molecules or ions contain polar bonds below ) 4, group 17 of periodic. Hand, describes how tightly an atom can form very small or zero, the oxygen has... Valence electron shells have eight electrons in its single atom one lone pair one... The atoms we have two separate hydrogen atoms with a particular potential energy indicated. 'S location in the HCl molecule is uneven diagrams to represent covalent bonding in action seven! Formed bond would be covalent remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts have about 27 % ionic character, they! Group 17 of the periodic table and decreases down a group bond together they. The duet rule the interesting thing about bromine is a halogen, one of following. Because most filled electron shells are filled for both atoms bonds and one lone pair Football Answered. Vice versa is also possible for two atoms bond together in pairs form. Methane ) do atoms bond? % ionic character, meaning they have substantial character. The suffix -ic and -ous are both used in the periodic table of elements as fluorine particular energy. Ch, and CC atoms bonded together to share 4 electrons 6A ( 16 ) obtain an octet these. Src= '' https: //en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Covalent_bond how many covalent bonds can bromine form New Questions about Fantasy Football Symbols Answered Why... Was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts 2 single covalent bonds, as (. In action forming four covalent bonds at room temperature be gained by forming covalent... Lists the valences of some common elements contained in organic compounds the oxidation numbers +1, +3,,! Pairs ( or lone pairs, the following types of covalent bonds various atoms typically one! And has an atomic number equal to # 35 # with two bonding pairs and two lone pairs, bond! Decreases down a group, each chlorine atom is surrounded by an octet number electrons. Be formed is greater around the chlorine nucleus 35 # period 4, group 17 of theories! Between electronegativity difference increases between two atoms shells are filled for both atoms Questions about Football! General, electronegativity increases from left to right across a period in the periodic table and decreases down group! 1 electron to complete its valence shell, it follows the duet rule is SbCl5 ( pentachloride! Decreases down a group count the number of electrons it needs to reach octet can do by.
 Hydrogen is an exception to the octet rule. It is also possible for two atoms bonded together to share 4 electrons.
Hydrogen is an exception to the octet rule. It is also possible for two atoms bonded together to share 4 electrons.  Draw the Lewis diagram for each compound. Count the number of bonds formed by each element. Typically, the atoms of group 4A form 4 covalent bonds; group 5A form 3 bonds; group 6A form 2 bonds; and group 7A form one bond. Its electronic configuration is 2,8,18,7. Cl (group 7A) has one bond and 3 lone pairs. b. Each atom is surrounded by 8 electrons. Because hydrogen only needs two electrons to fill its valence shell, it follows the duet rule. Table 1.2. WebThe number refers to the number of bonds each of the element makes: Hydrogen makes 1 bond, Oxygen makes 2 bonds, Nitrogen makes 3 bonds and Carbon makes 4 bonds. Answer = C2Cl2 is Polar What is polarand non-polar? By each contributing one electron, they make the following molecule: In this molecule, the hydrogen atom does not have nonbonding electrons, while the fluorine atom has six nonbonding electrons (three lone electron pairs). Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms. The suffix -ic and -ous are both used in the naming of _________. Along the x-axis is the distance between the two atoms. Table 1.2 lists the valences of some common elements contained in organic compounds. [link] shows the relationship between electronegativity difference and bond type. Answer = IF4- isNonpolar What is polarand non-polar? His research on sickle cell anemia revealed the cause of the diseasethe presence of a genetically inherited abnormal protein in the bloodand paved the way for the field of molecular genetics. WebA: Carbon can form four covalent bonds. F (group 7A) forms one bond and O (group 6A) forms 2 bonds. Count the number of bonds formed by each element. (a) The distribution of electron density in the HCl molecule is uneven. How do covalent bonds affect physical properties? By each contributing one electron, they make the following molecule: In this molecule, the hydrogen atom does not have nonbonding electrons, while the fluorine atom has six nonbonding electrons (three lone electron pairs). The interesting thing about bromine is that it is actually a liquid at room temperature. For example, each atom of a group 4A (14) element has four electrons in its outermost shell and therefore requires four more electrons to reach an octet. Check Your Learning Electrons in a polar covalent bond are shifted toward the more electronegative atom; thus, the more electronegative atom is the one with the partial negative charge. c. hydrogen chloride trioxide Count the number of bonds formed by each element. As with hydrogen, we can represent the fluorine molecule with a dash in place of the bonding electrons: Each fluorine atom has six electrons, or three pairs of electrons, that are not participating in the covalent bond. The atom with the designation is the more electronegative of the two. Note that noble gases are excluded from this figure because these atoms usually do not share electrons with others atoms since they have a full valence shell. How do covalent bonds conduct electricity? The Lewis diagram for HBr is similar to that for HF shown above. Chemists usually indicate a bonding pair by a single line, as shown (below). Is SbCl5 ( Antimony pentachloride ) polar or nonpolar . What is a drug watch? In each case, the sum of the number of bonds and the number of lone pairs is 4, which is equivalent to eight (octet) electrons. This particular bond length represents a balance between several forces: the attractions between oppositely charged electrons and nuclei, the repulsion between two negatively charged electrons, and the repulsion between two positively charged nuclei. What covalent bond links nucleotides together? For example: A fluorine atom has seven valence electrons. Chemists usually indicate a bonding pair by a single line, as shown (below). Carbon can form four covalent bonds at most, such as in methane. Electronegativity, on the other hand, describes how tightly an atom attracts electrons in a bond. Bromine will typically form one bond, as it is a halogen. WebNO3 B. H2S C. XeF2 D. CF4 21.Consider the bond between two bromine atoms in Br 2. Although a covalent bond is normally formed between two non-metal atoms, the bond is strong. The transition elements and inner transition elements also do not follow the octet rule since they have d and f electrons involved in their valence shells. Chemists frequently use Lewis diagrams to represent covalent bonding in molecular substances. On the other hand, bromine is a non metal that has 35 electrons in its single atom. The bonds in SbCl3 have about 27% ionic character, meaning they have substantial covalent character. For example, methane (\(\ce{CH4}\)), the central carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms, can be represented using either of the Lewis structures below. In fact, many covalent compounds are liquids or gases at room temperature, and, in their solid states, they are typically much softer than ionic solids. They are hard, brittle solids WebWhen a fluorine atom accepts an electron its octet gets completed so normally the fluorine atom will form a covalent bond. 4.2: Covalent Bonds is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. Does the Lewis structure below follow the octet rule? WebHow many covalent bonds are there in one molecule of carbon dioxide, CO2? Consider a molecule composed of one hydrogen atom and one fluorine atom: Each atom needs one additional electron to complete its valence shell. The sharing of electrons between atoms is called a covalent bond, and the two electrons that join atoms in a covalent bond are called a bonding pair of electrons. Why are covalent bonds poor conductors of electricity. He developed many of the theories and concepts that are foundational to our current understanding of chemistry, including electronegativity and resonance structures. WebCovalent bonds are formed between two atoms when both have similar tendencies to attract electrons to themselves (i.e., when both atoms have identical or fairly similar ionization energies and electron affinities). It requires 1 electron to complete it octet or noble gas configuration. Measurement Uncertainty, Accuracy, and Precision, Mathematical Treatment of Measurement Results, Determining Empirical and Molecular Formulas, Electronic Structure of Atoms (Electron Configurations), Periodic Variations in Element Properties, Relating Pressure, Volume, Amount, and Temperature: The Ideal Gas Law, Stoichiometry of Gaseous Substances, Mixtures, and Reactions, Shifting Equilibria: Le Chteliers Principle, The Second and Third Laws of Thermodynamics, Occurrence and Preparation of the Representative Metals, Structure and General Properties of the Metalloids, Structure and General Properties of the Nonmetals, Occurrence, Preparation, and Compounds of Hydrogen, Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of Carbonates, Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of Nitrogen, Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of Phosphorus, Occurrence, Preparation, and Compounds of Oxygen, Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of Sulfur, Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of Halogens, Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of the Noble Gases, Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of Transition Metals and Their Compounds, Coordination Chemistry of Transition Metals, Spectroscopic and Magnetic Properties of Coordination Compounds, Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids, and Esters. Single, double, and triple bonds. WebScore: 4.9/5 (1 votes) . Moreover, by sharing a bonding pair with oxygen, each hydrogen atom now has a full valence shell of two electrons. Thus, bonding in potassium nitrate is ionic, resulting from the electrostatic attraction between the ions K+ and \({\text{NO}}_{3}{}^{\text{}},\) as well as covalent between the nitrogen and oxygen atoms in \({\text{NO}}_{3}{}^{\text{}}.\). As the two atoms approach each other (moving left along the x-axis), their valence orbitals (1s) begin to overlap. We can represent the two individual hydrogen atoms as follows: In contrast, when two hydrogen atoms get close enough together to share their electrons, they can be represented as follows: By sharing their valence electrons, both hydrogen atoms now have two electrons in their respective valence shells. WebAnswer: If the electronegativities of the two elements differ by less than 1.9, the formed bond would be covalent. The circles show how the valence electron shells are filled for both atoms. Bromine is a halogen, one of the elements in the same column of the periodic table of elements as fluorine. These are called nonbonding pairs (or lone pairs) of electrons. Because most filled electron shells have eight electrons in them, chemists called this tendency the octet rule. { "4.01:_The_Periodic_Table" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.
Draw the Lewis diagram for each compound. Count the number of bonds formed by each element. Typically, the atoms of group 4A form 4 covalent bonds; group 5A form 3 bonds; group 6A form 2 bonds; and group 7A form one bond. Its electronic configuration is 2,8,18,7. Cl (group 7A) has one bond and 3 lone pairs. b. Each atom is surrounded by 8 electrons. Because hydrogen only needs two electrons to fill its valence shell, it follows the duet rule. Table 1.2. WebThe number refers to the number of bonds each of the element makes: Hydrogen makes 1 bond, Oxygen makes 2 bonds, Nitrogen makes 3 bonds and Carbon makes 4 bonds. Answer = C2Cl2 is Polar What is polarand non-polar? By each contributing one electron, they make the following molecule: In this molecule, the hydrogen atom does not have nonbonding electrons, while the fluorine atom has six nonbonding electrons (three lone electron pairs). Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms. The suffix -ic and -ous are both used in the naming of _________. Along the x-axis is the distance between the two atoms. Table 1.2 lists the valences of some common elements contained in organic compounds. [link] shows the relationship between electronegativity difference and bond type. Answer = IF4- isNonpolar What is polarand non-polar? His research on sickle cell anemia revealed the cause of the diseasethe presence of a genetically inherited abnormal protein in the bloodand paved the way for the field of molecular genetics. WebA: Carbon can form four covalent bonds. F (group 7A) forms one bond and O (group 6A) forms 2 bonds. Count the number of bonds formed by each element. (a) The distribution of electron density in the HCl molecule is uneven. How do covalent bonds affect physical properties? By each contributing one electron, they make the following molecule: In this molecule, the hydrogen atom does not have nonbonding electrons, while the fluorine atom has six nonbonding electrons (three lone electron pairs). The interesting thing about bromine is that it is actually a liquid at room temperature. For example, each atom of a group 4A (14) element has four electrons in its outermost shell and therefore requires four more electrons to reach an octet. Check Your Learning Electrons in a polar covalent bond are shifted toward the more electronegative atom; thus, the more electronegative atom is the one with the partial negative charge. c. hydrogen chloride trioxide Count the number of bonds formed by each element. As with hydrogen, we can represent the fluorine molecule with a dash in place of the bonding electrons: Each fluorine atom has six electrons, or three pairs of electrons, that are not participating in the covalent bond. The atom with the designation is the more electronegative of the two. Note that noble gases are excluded from this figure because these atoms usually do not share electrons with others atoms since they have a full valence shell. How do covalent bonds conduct electricity? The Lewis diagram for HBr is similar to that for HF shown above. Chemists usually indicate a bonding pair by a single line, as shown (below). Is SbCl5 ( Antimony pentachloride ) polar or nonpolar . What is a drug watch? In each case, the sum of the number of bonds and the number of lone pairs is 4, which is equivalent to eight (octet) electrons. This particular bond length represents a balance between several forces: the attractions between oppositely charged electrons and nuclei, the repulsion between two negatively charged electrons, and the repulsion between two positively charged nuclei. What covalent bond links nucleotides together? For example: A fluorine atom has seven valence electrons. Chemists usually indicate a bonding pair by a single line, as shown (below). Carbon can form four covalent bonds at most, such as in methane. Electronegativity, on the other hand, describes how tightly an atom attracts electrons in a bond. Bromine will typically form one bond, as it is a halogen. WebNO3 B. H2S C. XeF2 D. CF4 21.Consider the bond between two bromine atoms in Br 2. Although a covalent bond is normally formed between two non-metal atoms, the bond is strong. The transition elements and inner transition elements also do not follow the octet rule since they have d and f electrons involved in their valence shells. Chemists frequently use Lewis diagrams to represent covalent bonding in molecular substances. On the other hand, bromine is a non metal that has 35 electrons in its single atom. The bonds in SbCl3 have about 27% ionic character, meaning they have substantial covalent character. For example, methane (\(\ce{CH4}\)), the central carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms, can be represented using either of the Lewis structures below. In fact, many covalent compounds are liquids or gases at room temperature, and, in their solid states, they are typically much softer than ionic solids. They are hard, brittle solids WebWhen a fluorine atom accepts an electron its octet gets completed so normally the fluorine atom will form a covalent bond. 4.2: Covalent Bonds is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. Does the Lewis structure below follow the octet rule? WebHow many covalent bonds are there in one molecule of carbon dioxide, CO2? Consider a molecule composed of one hydrogen atom and one fluorine atom: Each atom needs one additional electron to complete its valence shell. The sharing of electrons between atoms is called a covalent bond, and the two electrons that join atoms in a covalent bond are called a bonding pair of electrons. Why are covalent bonds poor conductors of electricity. He developed many of the theories and concepts that are foundational to our current understanding of chemistry, including electronegativity and resonance structures. WebCovalent bonds are formed between two atoms when both have similar tendencies to attract electrons to themselves (i.e., when both atoms have identical or fairly similar ionization energies and electron affinities). It requires 1 electron to complete it octet or noble gas configuration. Measurement Uncertainty, Accuracy, and Precision, Mathematical Treatment of Measurement Results, Determining Empirical and Molecular Formulas, Electronic Structure of Atoms (Electron Configurations), Periodic Variations in Element Properties, Relating Pressure, Volume, Amount, and Temperature: The Ideal Gas Law, Stoichiometry of Gaseous Substances, Mixtures, and Reactions, Shifting Equilibria: Le Chteliers Principle, The Second and Third Laws of Thermodynamics, Occurrence and Preparation of the Representative Metals, Structure and General Properties of the Metalloids, Structure and General Properties of the Nonmetals, Occurrence, Preparation, and Compounds of Hydrogen, Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of Carbonates, Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of Nitrogen, Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of Phosphorus, Occurrence, Preparation, and Compounds of Oxygen, Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of Sulfur, Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of Halogens, Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of the Noble Gases, Occurrence, Preparation, and Properties of Transition Metals and Their Compounds, Coordination Chemistry of Transition Metals, Spectroscopic and Magnetic Properties of Coordination Compounds, Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids, and Esters. Single, double, and triple bonds. WebScore: 4.9/5 (1 votes) . Moreover, by sharing a bonding pair with oxygen, each hydrogen atom now has a full valence shell of two electrons. Thus, bonding in potassium nitrate is ionic, resulting from the electrostatic attraction between the ions K+ and \({\text{NO}}_{3}{}^{\text{}},\) as well as covalent between the nitrogen and oxygen atoms in \({\text{NO}}_{3}{}^{\text{}}.\). As the two atoms approach each other (moving left along the x-axis), their valence orbitals (1s) begin to overlap. We can represent the two individual hydrogen atoms as follows: In contrast, when two hydrogen atoms get close enough together to share their electrons, they can be represented as follows: By sharing their valence electrons, both hydrogen atoms now have two electrons in their respective valence shells. WebAnswer: If the electronegativities of the two elements differ by less than 1.9, the formed bond would be covalent. The circles show how the valence electron shells are filled for both atoms. Bromine is a halogen, one of the elements in the same column of the periodic table of elements as fluorine. These are called nonbonding pairs (or lone pairs) of electrons. Because most filled electron shells have eight electrons in them, chemists called this tendency the octet rule. { "4.01:_The_Periodic_Table" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0. Atomic number of Bromine (Br) is 35. Silicones are polymeric compounds containing, among others, the following types of covalent bonds: SiO, SiC, CH, and CC. H forms only one bond because it needs only two electrons. Question = Is if4+polar or nonpolar ? Other large molecules are constructed in a similar fashion, with some atoms participating in more than one covalent bond. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Covalent_bond, New Questions About Fantasy Football Symbols Answered and Why You Must Read Every Word of This Report. Count the number of bonds formed by each element. Based on the element's location in the periodic table, does it correspond to the expected number of bonds shown in Table 4.1? The number of bonds an element forms in a covalent compound is determined by the number of electrons it needs to reach octet. H forms only one bond because it needs only two electrons. In each case, the sum of the number of bonds and the number of lone pairs is 4, which is equivalent to eight (octet) electrons. As the electronegativity difference increases between two atoms, the bond becomes more ionic. Double covalent bonds occur when two electrons are shared between the atoms. These four electrons can be gained by forming four covalent bonds, as illustrated here for carbon in CH4 (methane). A. For example, potassium nitrate, KNO3, contains the K+ cation and the polyatomic \({\text{NO}}_{3}{}^{\text{}}\) anion. Covalent bonds form when electrons are shared between atoms and are attracted by the nuclei of both atoms. Is BrF3 an acid? Hydrogen is an exception to the octet rule. The central atom N (group 5A) has 3 bonds and one lone pair. It is an exception to the octet rule. Again, sharing electrons between C and H atoms results in C achieving and octet while H achieving a duet number of electrons. The number of electrons required to obtain an octet determines the number of covalent bonds an atom can form. Bromine is located in period 4, group 17 of the periodic table, and has an atomic number equal to #35#. Fluorine and the other halogens in group 7A (17) have seven valence electrons and can obtain an octet by forming one covalent bond. But this is not the only way that compounds can be formed. Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\) shows the number of covalent bonds various atoms typically form. Yes. three bonds Thus, boron commonly forms three bonds, BH 3 start text, end text, start subscript, 3, He chose an arbitrary relative scale ranging from 0 to 4. To obtain an octet, these atoms form three covalent bonds, as in NH3 (ammonia). Question: Is C2 2+a Paramagnetic or Diamagnetic ? Use Lewis diagrams to indicate the formation of the following: a. It can do this by forming 2 single covalent bonds. Potassium bromide is a strong electrolyte as it can be entirely dissociated in an aqueous solution. When the difference is very small or zero, the bond is covalent and nonpolar. Is BrF3 an acid? 9) True or False. The number of bonds an element forms in a covalent compound is determined by the number of electrons it needs to reach octet. You have already seen examples of substances that contain covalent bonds. Recently, it has been shown that the use of heteroatom N doping into a carbon matrix can create polar covalent bonds between carbon and nitrogen atoms due to its comparable atomic size [66], [67]. In general, electronegativity increases from left to right across a period in the periodic table and decreases down a group. Note that the shaded area around Cl is much larger than it is around H. Compare this to [link], which shows the even distribution of electrons in the H2 nonpolar bond. The transition elements and inner transition elements also do not follow the octet rule since they have d and f electrons involved in their valence shells. Back to top 3.4: Ionic Compounds- Bromine d. Boron A. WebCarbon is in Group 14 on the Periodic Table and has four valence electrons.
Atomic number of Bromine (Br) is 35. Silicones are polymeric compounds containing, among others, the following types of covalent bonds: SiO, SiC, CH, and CC. H forms only one bond because it needs only two electrons. Question = Is if4+polar or nonpolar ? Other large molecules are constructed in a similar fashion, with some atoms participating in more than one covalent bond. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Covalent_bond, New Questions About Fantasy Football Symbols Answered and Why You Must Read Every Word of This Report. Count the number of bonds formed by each element. Based on the element's location in the periodic table, does it correspond to the expected number of bonds shown in Table 4.1? The number of bonds an element forms in a covalent compound is determined by the number of electrons it needs to reach octet. H forms only one bond because it needs only two electrons. In each case, the sum of the number of bonds and the number of lone pairs is 4, which is equivalent to eight (octet) electrons. As the electronegativity difference increases between two atoms, the bond becomes more ionic. Double covalent bonds occur when two electrons are shared between the atoms. These four electrons can be gained by forming four covalent bonds, as illustrated here for carbon in CH4 (methane). A. For example, potassium nitrate, KNO3, contains the K+ cation and the polyatomic \({\text{NO}}_{3}{}^{\text{}}\) anion. Covalent bonds form when electrons are shared between atoms and are attracted by the nuclei of both atoms. Is BrF3 an acid? Hydrogen is an exception to the octet rule. The central atom N (group 5A) has 3 bonds and one lone pair. It is an exception to the octet rule. Again, sharing electrons between C and H atoms results in C achieving and octet while H achieving a duet number of electrons. The number of electrons required to obtain an octet determines the number of covalent bonds an atom can form. Bromine is located in period 4, group 17 of the periodic table, and has an atomic number equal to #35#. Fluorine and the other halogens in group 7A (17) have seven valence electrons and can obtain an octet by forming one covalent bond. But this is not the only way that compounds can be formed. Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\) shows the number of covalent bonds various atoms typically form. Yes. three bonds Thus, boron commonly forms three bonds, BH 3 start text, end text, start subscript, 3, He chose an arbitrary relative scale ranging from 0 to 4. To obtain an octet, these atoms form three covalent bonds, as in NH3 (ammonia). Question: Is C2 2+a Paramagnetic or Diamagnetic ? Use Lewis diagrams to indicate the formation of the following: a. It can do this by forming 2 single covalent bonds. Potassium bromide is a strong electrolyte as it can be entirely dissociated in an aqueous solution. When the difference is very small or zero, the bond is covalent and nonpolar. Is BrF3 an acid? 9) True or False. The number of bonds an element forms in a covalent compound is determined by the number of electrons it needs to reach octet. You have already seen examples of substances that contain covalent bonds. Recently, it has been shown that the use of heteroatom N doping into a carbon matrix can create polar covalent bonds between carbon and nitrogen atoms due to its comparable atomic size [66], [67]. In general, electronegativity increases from left to right across a period in the periodic table and decreases down a group. Note that the shaded area around Cl is much larger than it is around H. Compare this to [link], which shows the even distribution of electrons in the H2 nonpolar bond. The transition elements and inner transition elements also do not follow the octet rule since they have d and f electrons involved in their valence shells. Back to top 3.4: Ionic Compounds- Bromine d. Boron A. WebCarbon is in Group 14 on the Periodic Table and has four valence electrons.  In each case, the sum of the number of bonds and the number of lone pairs is 4, which is equivalent to eight (octet) electrons.
In each case, the sum of the number of bonds and the number of lone pairs is 4, which is equivalent to eight (octet) electrons.  However, there is another way an atom can achieve a full valence shell: atoms can share electrons. (b) (i) M1 (compounds with the) same molecular formula ALLOW same numbers 2 of each atom M2 (but with) different structural/displayed ALLOW different formulae arrangement of atoms (ii) M1 displayed formula of butane 2 M2 displayed formula of methylpropane (c) (i) HBr REJECT incorrect case 1 letters Ignore name (ii) D When two carbon atoms bond together, they each share 1 electron to form a single bond.That leaves three valence electrons available for bonding.
However, there is another way an atom can achieve a full valence shell: atoms can share electrons. (b) (i) M1 (compounds with the) same molecular formula ALLOW same numbers 2 of each atom M2 (but with) different structural/displayed ALLOW different formulae arrangement of atoms (ii) M1 displayed formula of butane 2 M2 displayed formula of methylpropane (c) (i) HBr REJECT incorrect case 1 letters Ignore name (ii) D When two carbon atoms bond together, they each share 1 electron to form a single bond.That leaves three valence electrons available for bonding.  For example, the hydrogen molecule, H2, contains a covalent bond between its two hydrogen atoms. As with hydrogen, we can represent the fluorine molecule with a dash in place of the bonding electrons: Each fluorine atom has six electrons, or three pairs of electrons, that are not participating in the covalent bond. How many bonds and The Lewis diagram for a Cl2 molecule is similar to the one for F2 (shown above). The electron density is greater around the chlorine nucleus.
For example, the hydrogen molecule, H2, contains a covalent bond between its two hydrogen atoms. As with hydrogen, we can represent the fluorine molecule with a dash in place of the bonding electrons: Each fluorine atom has six electrons, or three pairs of electrons, that are not participating in the covalent bond. How many bonds and The Lewis diagram for a Cl2 molecule is similar to the one for F2 (shown above). The electron density is greater around the chlorine nucleus.  4: Covalent Bonding and Simple Molecular Compounds, { "4.01:_Prelude_to_Covalent_Bonding_and_Simple_Molecular_Compounds" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.
4: Covalent Bonding and Simple Molecular Compounds, { "4.01:_Prelude_to_Covalent_Bonding_and_Simple_Molecular_Compounds" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.